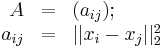Euclidean distance matrix
In mathematics, a Euclidean distance matrix is an n×n matrix representing the spacing of a set of n points in Euclidean space. If A is a Euclidean distance matrix and the points are defined on m-dimensional space, then the elements of A are given by
where ||.||2 denotes the 2-norm on Rm.
Properties
Simply put, the element aij describes the square of the distance between the i th and j th points in the set. By the properties of the 2-norm (or indeed, Euclidean distance in general), the matrix A has the following properties.
- All elements on the diagonal of A are zero (i.e. is it a hollow matrix).
- The trace of A is zero (by the above property).
- A is symmetric (i.e. aij = aji).
- aij1/2
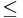 aik1/2 + akj1/2 (by the triangle inequality)
aik1/2 + akj1/2 (by the triangle inequality) 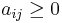
- The number of unique (distinct) non-zero values within an N-by-N Euclidean distance matrix is bounded (above) by [N*(N-1)] / 2 due to the matrix being symmetric and hollow.
See also
References
- James E. Gentle (2007). Matrix Algebra: Theory, Computations, and Applications in Statistics. Springer-Verlag. p. 299. ISBN 0387708723.